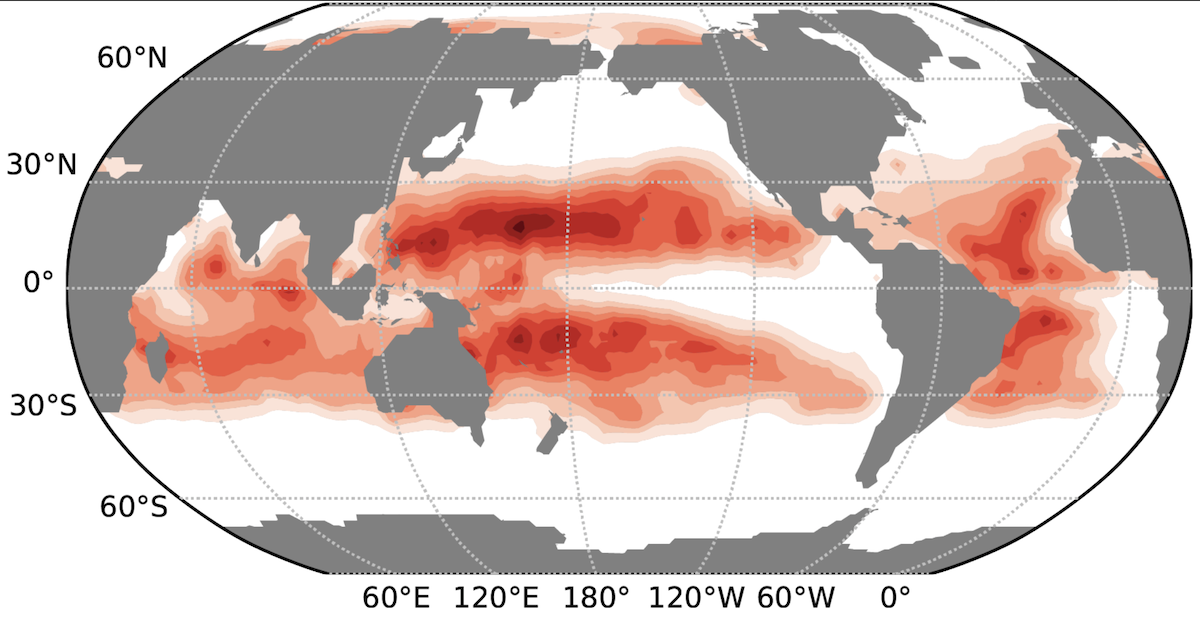
Uncertainty in the global patterns of marine nitrogen fixation limits our understanding of the response of the ocean’s nitrogen and carbon cycles to environmental change. The geographical distribution and ecological controls on nitrogen fixation are difficult to constrain with limited in-situ measurements. Here Prof. Primeau will present an inverse model to constrain the residual mean circulation of the ocean and to estimate rates of marine nitrogen fixation. The results demonstrate strong spatial variability in the nitrogen to phosphorus ratio of exported organic matter that greatly increases the global nitrogen-fixation rate. It is found that new nitrogen supports up to 50% of export in subtropical gyres, that nitrogen fixation and denitrification are spatially decoupled and that current-era nitrogen sources and sinks largely balance on multidecadal timescales. These findings suggest higher than expected ocean carbon export and weaker stabilizing nitrogen-cycle feedbacks than previously thought.
Speaker Biography:
Francois Primeau is a Professor of Earth System Science at the University of California, Irvine. His research is at the interface between physical oceanography and biogeochemistry where he develops computational methods to make better inferences from data and models about the physical and biogeochemical state of the ocean.