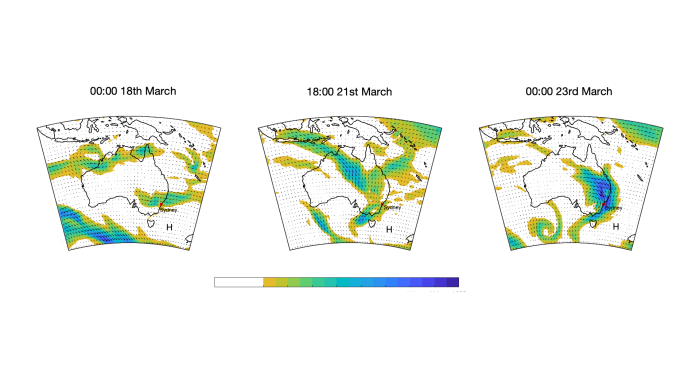
Between the 17th and 24th of March 2021, eastern Australia experienced record-breaking rainfall and widespread flooding; more than 400mm of rain fell in some locations.
The cause was a confluence of moisture in the atmosphere from two different sources.
A high-pressure system in the Tasman Sea pushed moist air over the coast from the east.
From the west, moisture was transported from the Indian Ocean by an Atmospheric River.
Atmospheric Rivers are streamers of moist air in the lower atmosphere that transport water vapour from the Tropics.
They can cause heavy rainfall, flooding, landslides, strong winds and heavy snowfalls.
New research by the ARC Centre of Excellence for Climate Extremes has shown that the probability of weather events like the one that caused the extreme rainfall in March 2021 could increase by 80% over Sydney by the end of the 21st century due to climate change.
