-
Research brief: How warm water reaches Antarctica

Using a high-resolution ocean model, CLEX researchers unexpectedly found 80% of the transport in the warm water layer, known as Circumpolar Deep Water, approaches Antarctica in the colder regions.
-
Climate change and natural variability behind ocean warming anomaly

New study finds ocean heat asymmetry between hemispheres can be explained by natural variability in the climate system superimposed on long-term ocean warming.
-
Research brief: CMIP5 and CMIP6 Projections of Australia’s future climate compared
CLEX authors and colleagues from major Australian science organisations investigating climate examined the simulation of Australian climate in the new, state-of-the-art Coupled Model Intercomparison Project, phase 6 (CMIP6) models.
-
Research brief: SSTs create biases in how ENSO appears in CMIP5 models

A new study by CLEX researchers and colleagues shows that CMIP5 models as a group, when forced by observed sea surface temperatures underestimate, these atmospheric feedbacks on average by 23%. This underestimate can be linked to the wrong location at which climate models simulate the most important tropical circulation, called the Walker circulation.
-
Indian Ocean phenomenon spells climate trouble for Australia

New international research has found a worrying change in the Indian Ocean’s surface temperatures that puts southeast Australia on course for increasingly hot and dry conditions.
-
Research brief: Flexible definitions needed for fronts in Southern Ocean

This paper is a review article that stemmed from a debate within the Southern Ocean community. The paper explains how “fronts”, sharp boundaries between water masses, are defined, and what their effects might be on the biology of the Southern Ocean.
-
Research brief: Algorithm improvements reduce errors in ocean chlorophyll observations
CLEX researchers evaluate the performance of satellite chlorophyll observations in the tropical Pacific Ocean and suggest algorithm improvements.
-
Research brief: Climate change to slow Indian Ocean circulation

Climate models project that all circulation features of the South Indian Ocean, including the Leeuwin Current and Undercurrent, North and South East Madagascar Currents, transport through the Mozambique Channel and Agulhas Current are projected to weaken significantly in the last half of the 21st century with unchecked greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Montreal Protocol set to slow global warming by at least 1°C

The Montreal Protocol, an international agreement signed in 1987 to stop chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) destroying the ozone layer, now appears to be the first international treaty to successfully slow the rate of global warming.
-
Research brief: How magnetic fields can make water behave like honey
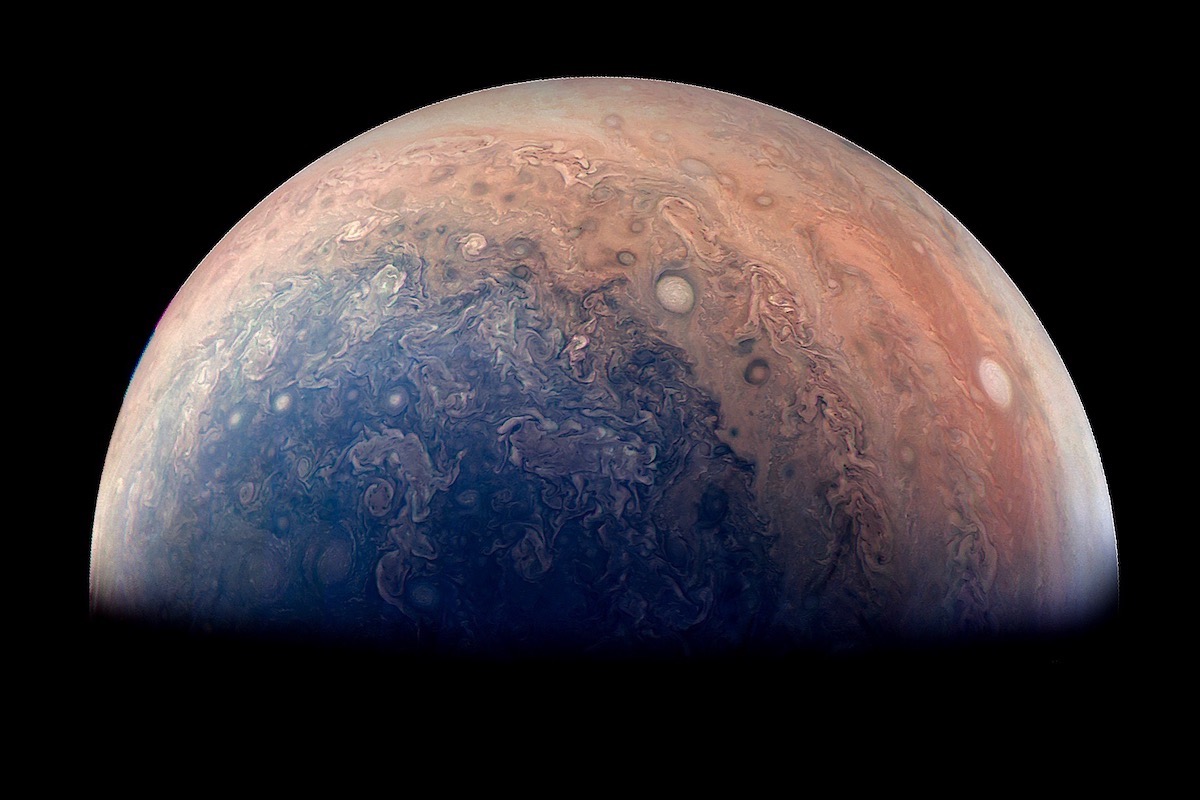

Turning on a magnetic field may make fluids that conduct electricity behave more like honey than like water. This discovery may help explain a mystery of Jupiter’s zonal winds, the alternating east-west jet streams, seen in photographs as colourful stripes.
