 August 17, 2021 10:38 am
Published by Climate Extremes
August 17, 2021 10:38 am
Published by Climate Extremes
The ocean’s much larger heat capacity acts as “memory” suppressing the atmosphere’s “high-frequency variability” (over time scales of weeks) while producing oceanic motions that vary over longer time scales. This paradigm aims to explain how low-frequency variability emerges in the ocean. But, recently, this paradigm has been challenged.
 August 28, 2020 9:30 am
Published by Climate Extremes
August 28, 2020 9:30 am
Published by Climate Extremes
High resolution ocean modelling has found the world’s strongest ocean currents, which play key roles in fisheries and ocean ecosystems, will experience more intense marine heatwaves than the global average over coming decades.
 August 3, 2020 4:48 pm
Published by Climate Extremes
August 3, 2020 4:48 pm
Published by Climate Extremes
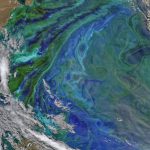
CLEX researchers used real-world observations with satellite observations to calculate the quantity of nutrients carried into the Subantarctic Zone by mesoscale eddies. They found these eddies carried high nitrate and low silicate waters into the Subantarctic Zone.
 November 25, 2019 2:34 pm
Published by Climate Extremes
November 25, 2019 2:34 pm
Published by Climate Extremes
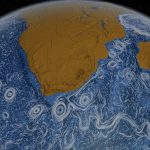
CLEX researchers investigate the physics of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current to understand why increased wind stress doesn't lead to a more powerful current. It turns out the ocean floor plays a key role.
 September 6, 2019 2:40 pm
Published by Climate Extremes
September 6, 2019 2:40 pm
Published by Climate Extremes
In this study, CLEX researchers use two years of measurements from a flux mooring combined with satellite data and model outputs to understand the seasonal changes in air‐sea fluxes and the role of ocean currents in controlling ocean surface temperatures in the southeast Indian Ocean.
 November 30, 2018 12:57 pm
Published by Climate Extremes
November 30, 2018 12:57 pm
Published by Climate Extremes
It has been a very active time for the Climate Variability and Teleconnections Research Program in terms of research and engagement activities right across the team, including two expeditions - one drilling coral cores in the tropics and another going south to the Antarctic Circumpolar Current.
 August 15, 2018 10:43 am
Published by Climate Extremes
August 15, 2018 10:43 am
Published by Climate Extremes
CLEX researchers found that counter-clockwise rotating eddies in the Southern Ocean mix the ocean deeper in winter, allowing more nutrients to enter their interiors, leading to higher productivity. This work is important because eddy productivity plays a significant role in the exchange of carbon between the ocean and the atmosphere.
 April 11, 2018 12:50 am
Published by Climate Extremes
April 11, 2018 12:50 am
Published by Climate Extremes
Students and ECRs have an opportunity to take part in a voyage to a standing meander of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) south of Tasmania. They will undertake a 3-dimensional survey of the velocity and density structure of the meander, deploy a fleet of EM-APEX profiling floats and conduct time series measurements.








